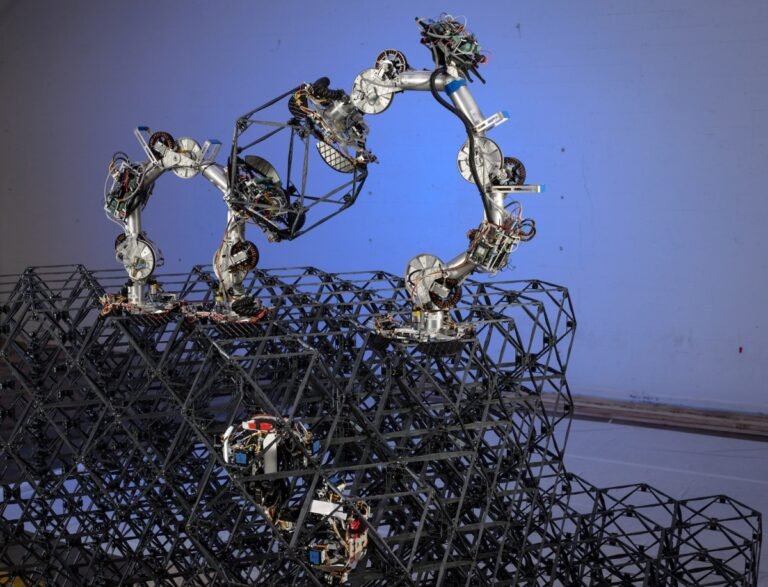
Fortunately, NASA (as as always) is thinking ahead, and has just shown off a self-assembling robotic structure that might just be a crucial part of moving off-planet.
“We think this type of construction technology can serve a lot of very general applications,” said lead author Christine Gregg.
“In the near term, the robust autonomy and lightweight structures of our approach strongly benefit applications in austere environments, like the lunar surface or space.
“For us, the structures and all of the robotic systems are resources that can be optimized over space and time.
Versions of the robot have already flown in space and done work in microgravity, so no worries on that score.

Isomorphic Labs, the London-based, drug discovery-focused spin-out of Google AI R&D division DeepMind, today announced that it’s entered into strategic partnerships with two pharmaceutical giants, Eli Lilly and Novartis, to apply AI to discover new medications to treat diseases.
Isomorphic will receive $45 million upfront from Eli Lilly and potentially up to $1.7 billion based on performance milestones, excluding royalties.
Researchers recently used AlphaFold to design and synthesize a potential drug to treat hepatocellular carcinoma, the most common type of primary liver cancer.
The latest version of AlphaFold can generate predictions for nearly all molecules in the Protein Data Bank, the world’s largest open access database of biological molecules, DeepMind announced in late October.
Already, Isomorphic is applying the new AlphaFold model, which it co-designed with DeepMind, to therapeutic drug design, helping to characterize different types of molecular structures important for treating disease.





