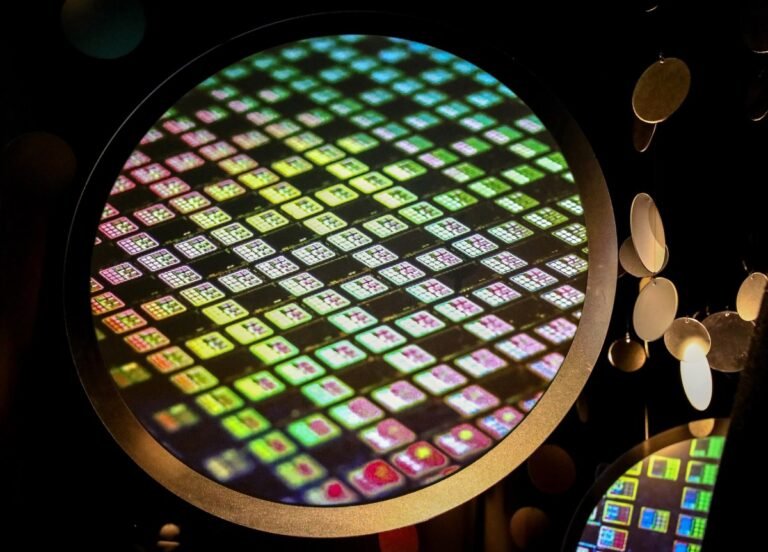
This grant, pegged for the company’s U.S. subsidiary, TSMC Arizona, is the latest step by the U.S. to strengthen its domestic supply of semiconductors as it seeks to reshore manufacturing of chips amid escalating geopolitical tensions between the U.S. and China.
The Act is primarily aimed at attracting manufacturing stateside, and also prohibits recipients of the funding from increasing their semiconductor manufacturing footprint in China.
With the new investment, Taiwan-based TSMC, which is the world’s largest producer of semiconductors, is broadening its plans for its fabrication plants in Arizona.
Intel could receive approximately $20 billion in grants and loans from the CHIPS and Science Act for its semiconductor manufacturing.
Meanwhile, Samsung, which announced a $17 billion additional investment in Taylor, Texas, is expected to receive more than $6 billion in grants for its chip facility in Texas.

Seven open source foundations are coming together to create common specifications and standards for Europe’s Cyber Resilience Act (CRA), regulation adopted by the European Parliament last month.
And this is what the seven open source foundations are coming together for now.
By coming together as one, this should go some way toward treating open source software development as a single “thing” bound by the same standards and processes.
Throw into the mix other proposed regulation, including the Securing Open Source Software Act in the U.S., and it’s clear that the various foundations and “open source stewards” will come under greater scrutiny for their role in the software supply chain.
“The open source community and the broader software industry now share a common challenge: legislation has introduced an urgent need for cybersecurity process standards.

March 29 is the final day to grab your early-bird savings for TechCrunch Early Stage 2024.
TechCrunch Early Stage 2024 is set to take place in Boston, offering invaluable resources and insights for founders at every stage of their journey.
Here’s what awaits you at TechCrunch Early StageRoundtable sessions: Engage in collaborative conversations with experts in small-group settings.
Don’t wait until it’s too late — secure your tickets now and accelerate your startup journey at TechCrunch Early Stage 2024!
Is your company interested in sponsoring or exhibiting at TechCrunch Early Stage 2024?

The CHIPS Act can be seen as a direct result of a number of pressing geopolitical issues.
The above, coupled with long-standing efforts to revitalize U.S. industry, spurred on economic efforts to reshore manufacturing.
While the CHIPS Act was still winding its way through Capitol Hill, Intel announced plans to open a $10 billion manufacturing facility just outside of Columbus, Ohio.
It says it expects those efforts will create 20,000 construction and 10,000 manufacturing jobs — music to the ears of an administration keenly focused on monthly jobs reports.
Notably, Intel recently pushed back the manufacturing start date of its New Albany, Ohio, plant two years to 2027, citing changes to the business environment.

The European Parliament voted Wednesday to adopt the AI Act, securing the bloc pole-position in setting rules for a broad sweep of artificial intelligence-powered software — or what regional lawmakers have dubbed “the world’s first comprehensive AI law”.
pic.twitter.com/t4ahAwkaSn — Thierry Breton (@ThierryBreton) March 13, 2024Once published in the EU’s Official Journal in the coming months, the AI Act will come into force 20 days after that.
And with that alone the AI Act has nudged the future of AI in a human-centric direction.
But the legislation also puts some (light touch) transparency obligations on a third subset of apps, including AI chatbots; generative AI tools that can create synthetic media (aka deepfakes); and general purpose AI models (GPAI).
Rules for GPAIs were a later addition to the AI Act, driven by concerned MEPs.

Bumble has lost a third of its Texas workforce in the months since the state passed the controversial abortion SB 8 (Senate Bill 8), also known as the Texas Heartbeat Act, over a year ago.
We’ve supported employees who’ve chosen to move out of state,” Monteleone added.
“We — since SB 8 — have seen a reduction in our Texas workforce by about a third.
The dating app maker became the first business to join an amicus brief in support of a lawsuit against the Texas abortion law, Zurawski v. State of Texas, filed by the Center for Reproductive Rights.
The dating app maker posted a weak Q4, with a $32 million net loss and $273.6 million in revenue.

Eva Maydell is a Bulgarian politician and a member of European Parliament.
Eva Maydell, member of European ParliamentBriefly, how did you get your start in AI?
When I first became a member of the European Parliament, I was one of the few young female members of European Parliament (MEPs) that worked on tech issues.
The more women keep sharing their ideas, visions and voice, the more they will inspire other women to step into the world of tech.
The greatest challenge for any politician working on tech and AI is trying to regulate and prepare for the future with accuracy.

South Korean internet giant Kakao — in the middle of multiple investigations over antitrust and securities violations — has appointed a new CEO as it tries to turn the ship around.
Shina Chung, who had been running the company’s venture arm, is moving to the top role at the company.
Separately, just last month, South Korean President Yoon Suk Yeol called for a review of the monopolistic practices of Kakao’s taxi-hailing unit, Kakao Mobility.
Korea’s antitrust regulator had already fined Kakao Mobility about $20.3 million for unfair service in February.
Kakao Mobility, which has about 74% of the ride-hailing market in the country as of September, separately is trying to lower the temperature around this controvery.

An industry group representing major tech firms such as Google, Meta and Amazon has denounced an Indian parliamentary panel’s proposed digital competition law. Claiming the proposal is “absolutist and regressive,”…












