
Wastewater from these plants emerges laden with sodium sulfate, a byproduct of sulfuric acid and caustic soda, two chemicals used in battery manufacturing, copper refining and other industries.
“We can totally create a circular economy around these reagent chemicals,” Bilen Akuzum, co-founder and CTO of Aepnus Technology, told TechCrunch.
The two founded Aepnus to modernize the century-old chloralkali process, which splits salts like sodium sulfate back into the acids and bases that created them.
“We don’t use any expensive catalysts in our electrolyzers,” Akuzum said.
For customers, fully recycling sodium sulfate waste should reduce disposal and material costs.

It was while sourcing manufacturing equipment for Tesla factories that Will Drewery drew inspiration for Diagon, a startup that helps manufacturers procure equipment.
Companies in fields like automotive and aerospace can identify qualified suppliers from Diagon’s network of equipment suppliers, system integrators and service providers.
East Coast originsThe journey to Diagon for Drewery, who spent most of his career as an equipment buyer, started in Pittsburgh.
“This is why I felt the market needs a Diagon,” Drewery said.
“Now we are developing tools that help customers find suppliers better or help them interpret and summarize quotes better,” Drewery said.

The United States Department of Commerce Monday proposed investing as much as $6.6 billion to fund a third Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company Limited (TSMC) fab in Arizona.
The move represents a broader push to bring more manufacturing to the U.S., but unspoken in the fanfare around today’s announcement is the potential escalation of tensions with China.
TSMC Arizona — the subsidiary behind the proposed construction — has stated that it will build the facility before the end of the decade.
The United States and allies would be at a massive disadvantage should China seize control of Taiwan and its manufacturing capabilities.
For all the money the United States government continues to invest, Intel is simply playing catch-up to TSMC’s multiyear technological head start.
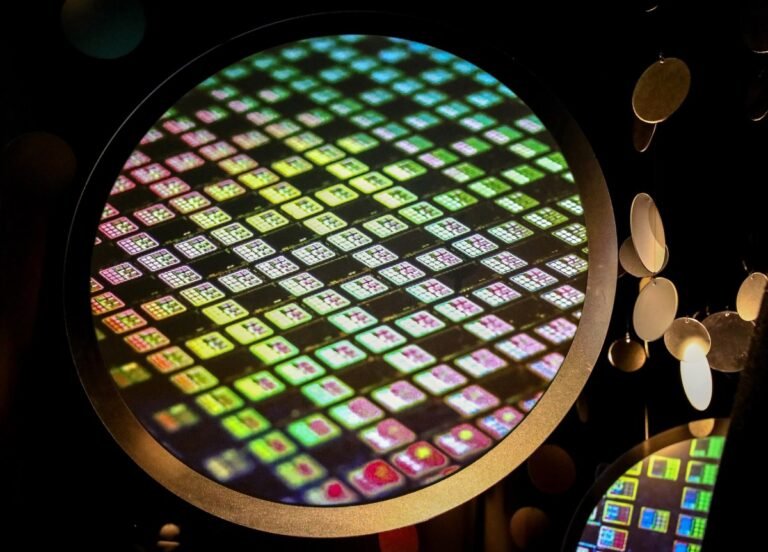
This grant, pegged for the company’s U.S. subsidiary, TSMC Arizona, is the latest step by the U.S. to strengthen its domestic supply of semiconductors as it seeks to reshore manufacturing of chips amid escalating geopolitical tensions between the U.S. and China.
The Act is primarily aimed at attracting manufacturing stateside, and also prohibits recipients of the funding from increasing their semiconductor manufacturing footprint in China.
With the new investment, Taiwan-based TSMC, which is the world’s largest producer of semiconductors, is broadening its plans for its fabrication plants in Arizona.
Intel could receive approximately $20 billion in grants and loans from the CHIPS and Science Act for its semiconductor manufacturing.
Meanwhile, Samsung, which announced a $17 billion additional investment in Taylor, Texas, is expected to receive more than $6 billion in grants for its chip facility in Texas.

Today, large swaths of the globe haven’t adopted air-source heat pumps because they don’t work as well when the mercury drops.
What’s more, the refrigerants most heat pumps use are either potent greenhouse gases or can break down into forever chemicals, researchers have found.
Heat pumps are used not just to heat and cool homes and vehicles, but also to generate heat for industrial processes, dehumidify buildings, keep food cold in grocery stores, and more.
The Biden administration announced in February that it was devoting $63 million from the Defense Production Act to boost heat pump manufacturing specifically.
Now it just has to get its super-fast compressors into production in time to catch the wave of heat pump adoption.

In an alkaline electrolyzer, two electrodes are submerged in a solution of alkaline water (usually consisting of a high concentration of potassium or sodium hydroxide).
Alkaline electrolysis differs from the other main approach, proton-exchange membrane electrolysis, in a few ways.
One of the most important, though, is that alkaline electrolysis doesn’t require expensive exotic metals like platinum.
That gives alkaline electrolyzers a cost advantage from the start, one that Evoloh says it builds on with its lower-cost manufacturing.
To further trim manufacturing costs, Evoloh uses roll-to-roll printing, a technique pioneered centuries ago by printing presses and more recently used in battery manufacturing.

The CHIPS Act can be seen as a direct result of a number of pressing geopolitical issues.
The above, coupled with long-standing efforts to revitalize U.S. industry, spurred on economic efforts to reshore manufacturing.
While the CHIPS Act was still winding its way through Capitol Hill, Intel announced plans to open a $10 billion manufacturing facility just outside of Columbus, Ohio.
It says it expects those efforts will create 20,000 construction and 10,000 manufacturing jobs — music to the ears of an administration keenly focused on monthly jobs reports.
Notably, Intel recently pushed back the manufacturing start date of its New Albany, Ohio, plant two years to 2027, citing changes to the business environment.

Apple has added another AI startup to its acquisition list with Canada-based DarwinAI, which specializes in vision-based tech to observe components during manufacturing to improve efficiency, Bloomberg reported.
DarwinAI had raised over $15 million in funding across various rounds from investors including BDC Capital’s Deep Tech Venture Fund, Honeywell Ventures, Obvious Ventures, and Inovia Capital.
BDC Capital and Obvious Venture didn’t comment on the story at the time of writing.
As Bloomberg noted in its report, apart from helping with manufacturing efficiency, DarwinAI uses techniques to make AI models smaller and faster.
This could be useful for on-device generative AI features Apple hopes to introduce in iOS 18 this year.

Almost a decade ago, Desktop Metal was one of the early darlings in accessible 3D printing in metal.
Last year, Stratasys tried to merge with Desktop Metal in a $1.8 billion deal, but the deal fell through, and these days, Desktop Metal is worth less than $210 million.
In June 2020, he split off and started his own thing — Fluent Metal — which is taking a different technology path than Desktop Metal’s technology.
It accomplishes this through liquid metal printing technology, which it hopes will set a new standard in additive manufacturing.
“In the near term, Fluent Metal will spark the imagination of designers, engineers, and technologists to consider how rapid, on-demand production of custom metal parts could transform their capabilities.
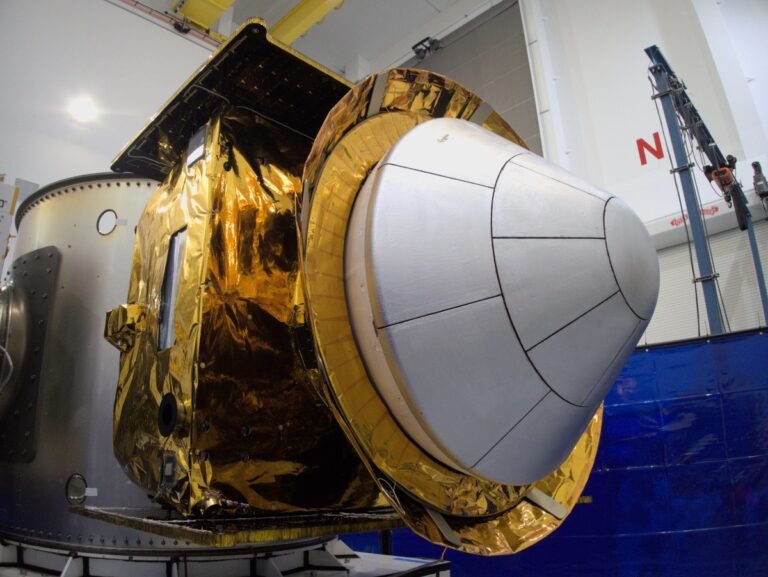

A spacecraft containing pharmaceutical drugs that were grown on orbit has finally returned to Earth today after more than eight months in space.
Varda Space Industries’ in-space manufacturing capsule, called Winnebago-1, landed in the Utah desert at around 4:40 p.m. EST.
The first-of-its-kind reentry and landing is also a major win for Rocket Lab, which partnered with Varda on the mission.
Rocket Lab hosted Varda’s manufacturing capsule inside its Photon satellite bus; through the course of the mission, Photon provided power, communications, attitude control and other essential operations.
Varda’s mission launched on June 12 and was supposed to be just a month long, but it was extended after the company encountered regulatory issues.













